The clothing industry is rapidly evolving, driven by innovations in technology. The Clothing Printing Machine represents a significant advancement in this sector. According to a recent report by Smith & Associates, the global market for clothing printing machines is projected to reach $4 billion by 2025, showcasing a CAGR of 14%. This growth reflects the increasing demand for customized apparel and rapid production.
John Thompson, a leading expert in textile technology, emphasizes, “The Clothing Printing Machine is revolutionizing how brands approach fabric printing.” His insight highlights the machine's ability to produce high-quality designs while reducing waste. As more businesses adopt these technologies, the challenges of sustainability and efficiency come into play.
However, the transition to these machines is not without obstacles. Some companies struggle to adapt their workflows, causing delays in production. Despite these issues, the potential for innovation in the clothing printing industry remains immense. Through continuous improvement, the Clothing Printing Machine may reshape the future of fashion.

A clothing printing machine is a specialized device used to apply designs onto fabric. It can be found in various forms, from screen printing to digital printing. Each type has its own unique capabilities and limitations. These machines can create vibrant colors and intricate designs. The process often involves preparing the fabric, aligning it properly, and setting the machine to the desired specifications.
For many, operating a clothing printing machine can feel overwhelming. The setup requires careful calibration. Colors may not always print as expected. Designs might not align perfectly during initial attempts. It’s essential to experiment and learn from these challenges. Mistakes are part of growing in this craft. Each print can teach a lesson, refining skills over time.
Additionally, different fabrics respond uniquely to printing techniques. Some materials may absorb ink better than others. Understanding these nuances enhances the final product. There is a certain satisfaction in correcting errors and finding the right methods. The journey of mastering a clothing printing machine is filled with trial and error, ultimately leading to artistic growth.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Printing Technologies | Common technologies include Direct to Garment (DTG), Screen Printing, and Sublimation printing. |
| Applications | Used for custom apparel, promotional products, and fashion design. |
| Materials | Compatible with various fabrics including cotton, polyester, and blends. |
| Print Quality | High-resolution printing for detailed designs and vibrant colors. |
| Speed | Can produce several garments per hour, depending on the technology used. |
| Cost | Initial investment varies widely; operational costs include ink and maintenance. |
| Software | Most machines come with compatible design software to create artwork. |
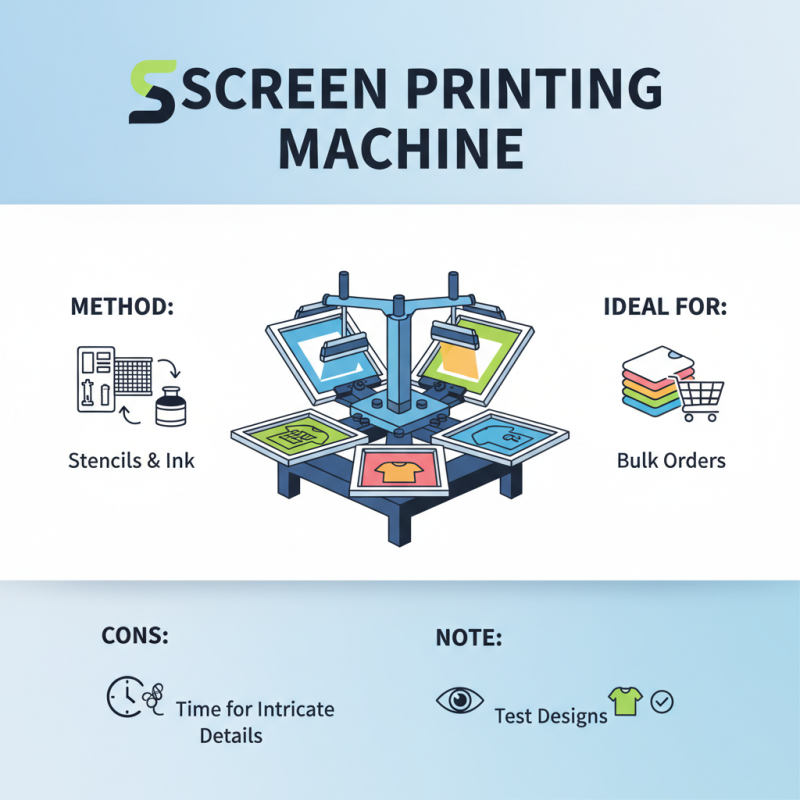
When exploring clothing printing machines, various types stand out. One popular option is the screen printing machine. This method uses stencils and ink to create designs. It’s ideal for bulk orders, but can be time-consuming for intricate details. Some designs may not translate well, so testing is essential.
Another significant type is digital printing. Unlike screen printing, it allows for high-detail images. This method uses specialized inkjet technology. It’s great for smaller runs or personalized items. However, the initial setup can be tricky, requiring careful calibration. Sometimes, colors may not appear as vibrant on fabric.
Heat transfer printing is another choice. This technique involves transferring a design from a special paper onto fabric using heat. It’s user-friendly and suitable for various materials. But durability can be an issue, as prints may fade over time. Each method has its pros and cons, and the choice depends on the project's specific needs.
The printing process in clothing production is a blend of art and technology. It begins with the design phase, where concepts transform into digital files. According to industry reports, approximately 70% of all garment printing now occurs digitally. This shift allows for intricate designs that meet evolving consumer preferences.
Once the design is ready, it moves to the printer. Here, specialized inks are applied to fabrics. Different printing techniques are used, such as direct-to-garment (DTG) and heat transfer. Each method has its benefits. DTG offers high detail, while heat transfer is often quicker. Studies show that companies using these technologies can reduce printing time by 50%. However, not all providers master these techniques, leading to variable outcomes.
Finally, curing or drying the print is crucial. This step doesn't get enough attention. Insufficient curing can result in fading or peeling, impacting the garment's lifespan. Yet, some manufacturers underestimate this stage. Their lack of focus can affect customer satisfaction. Quality control is essential. Advanced machinery can streamline processes, but it's not a foolproof solution. Continuous improvement is necessary for long-term success in this evolving field.
This chart displays the frequency of different clothing printing techniques used in the industry. Direct-to-Garment printing leads with 30%, followed by Screen Printing and Heat Transfer, indicating the preferred methods in the market.
Modern clothing printing machines have transformed the garment industry. They offer various features that enhance both efficiency and creativity. One key feature is high-speed printing. These machines can print designs quickly. This is essential for meeting customer demands in a fast-paced market.
Another important aspect is precision. Modern machines utilize advanced technology for accurate color placement. This ensures the designs come out as intended. The ability to print on various fabric types is also crucial. From cotton to polyester, these machines adapt well, widening design possibilities.
Tips for those considering a clothing printing machine: research the types of fabrics you plan to use. Not all machines work well with every material. Also, consider the initial investment versus long-term costs. Sometimes, cheaper machines don’t deliver on quality over time. Additionally, keep in mind that training is vital. Adequate training can make a substantial difference in print quality and operational efficiency.
Clothing printing technology is revolutionizing the fashion industry. It allows designers to create unique designs quickly and efficiently. This technology includes various methods, such as screen printing and direct-to-garment printing. Each method has its unique applications and benefits.
One key application of clothing printing is customization. Consumers now expect personalized products. With printing technology, brands can easily fulfill these demands. This enhances customer satisfaction and fosters brand loyalty. Additionally, small businesses can offer niche designs without large investments. They can print on-demand, minimizing waste and unsold inventory.
Tips: Always test designs on fabric before mass production. This helps catch any errors early. Consider the target audience. Their preferences should influence design choices. Experimentation is important, but always align it with market trends. Be cautious about over-complicating designs. Simple patterns often resonate more with customers.
Another advantage is the speed of production. Traditional methods can be time-consuming. Printing technology can produce items in a fraction of the time. Fast turnaround times could lead to increased sales. However, quality control is crucial. Poorly printed items can damage a brand’s reputation. Always prioritize quality, even in high-speed environments.






